What comes to your mind when you hear of Verifiable Credentials?

Chances are you have been hearing of the term Verifiable Credentials (VCs) or perhaps, it is an entirely new term to you. Either way, you are in the right place, as this article aims to explain the concepts of Verifiable Credentials and their applications.
However, before making a dive into the details of VCs, a quick background knowledge of Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Digital Identity is crucial. Another unfamiliar term? Well, I’ve got you! :)
In the digital realm, DIDs and VCs are fundamental concepts in identity management, paving the way for a secure and decentralized digital future. We are fully cognizant of the advancements we have made with the web. The transition from web2 to web3 has been particularly noteworthy and has greatly influenced the digital space, facilitating the development and adoption of digital identity solutions.
Digital Identity
Our online presence and traits, commonly referred to as Digital Identities, play a significant role in shaping our interactions and activities on the internet. Digital identities are the virtual representation of individuals or organizations, and they encompass various forms of credentials, such as passports, college certificates, driver's licenses, birth certificates, digital signatures, biometric data, and other digital footprints that collectively contribute to our digital presence.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
DIDs have emerged as unique identifiers to ensure privacy and control over our digital data. These identifiers empower individuals and organizations to have direct control over their digital identities and associated data, enhancing security and eliminating reliance on centralized authorities. DIDs can contain additional metadata, including service endpoints or public keys, providing valuable information about the associated digital identity.
Given the multitude of digital footprints available, it became imperative to establish methods for verifying and ensuring the integrity of this data, leading to the emergence of Verifiable Credentials (VCs).
Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
VCs complement DIDs by offering a means to ensure the accuracy and validity of digital claims. VCs serve as credentials that can be issued by organizations or self-sovereign identity systems. They are cryptographically signed, making them tamper-proof and reliable in verifying the authenticity, integrity, and validity of the underlying digital identity. There are different frameworks and standards for creating and using VCs. However, the most widely adopted and supported standard is the w3c specifications, which are considered a recommended approach for interoperability and standardization.
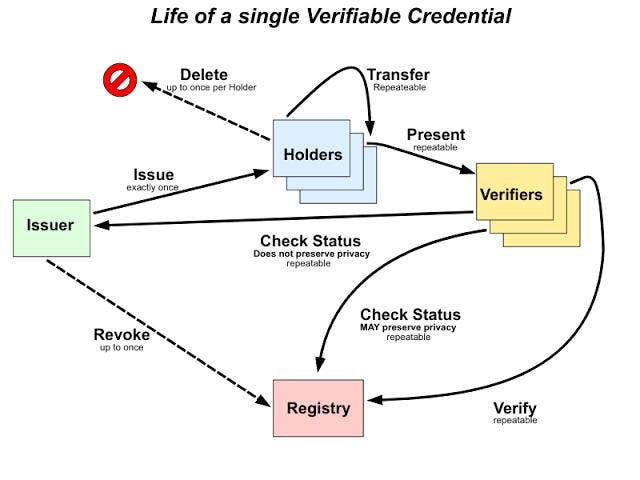
Demystifying the Key Players in Verifiable Credentials
Issuer: The issuer is the entity responsible for issuing the verifiable credential, such as a government agency or an educational institution.
Holder: The holder is the individual or organization possessing the VC.
Verifier: The verifier, often a service provider or an organization, checks the validity of the VC, ensuring it has not been revoked or expired.
Subject: This refers to the entity to whom the VC pertains, which can be either an individual or an organization.
Harnessing VCs
One key application of VCs is password-less logins. By leveraging VCs, individuals can prove their identity without relying on traditional username and password combinations, enhancing security and convenience. VCs also find utility in loan operations and applications, as they provide a trusted and immutable record of an individual's financial history and credibility.
Other use cases include:
Healthcare Data Sharing: VCs enable the secure sharing of medical records and vaccination data.
Supply Chain Management: VCs ensure product authenticity and integrity in supply chains.
Government Services: VCs streamline access to government services and processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Digital Identities, DIDs, and VCs are essential elements of identity management in the digital realm. DIDs enable individuals and organizations to have control and privacy over their digital identities, while VCs provide a means to verify the accuracy and validity of digital claims. By embracing these concepts, we can unlock a future where digital data is secure, decentralized, and empowers individuals and organizations alike.

